Daily Flyer - February 13, 2026
A voice of Ukraine to the West

,
Nearly 11,000 North Korean troops were deployed in Russia's Kursk Oblast at the beginning of 2026
About 11,000 North Korean troops are currently stationed in Russia’s Kursk Oblast to support Moscow’s war against Ukraine, South Korea’s Yonhap news agency reported on Feb. 12, citing the country’s National Intelligence Service (NIS).
According to the NIS, the contingent includes around 10,000 combat troops and 1,000 engineering personnel deployed in the frontline Russian region. Pyongyang has deepened its military cooperation with Moscow since the start of Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine, supplying weapons and sending troops in 2024. The intelligence agency also reported that roughly 1,100 North Korean soldiers who returned home from the front in December 2025 may be redeployed to Russia.
South Korean intelligence estimates that North Korean losses in Kursk Oblast have reached about 6,000 troops killed or injured. Despite the heavy casualties, the NIS assessed that North Korea has gained experience in modern combat tactics and battlefield operations, as well as technical assistance from Russia to upgrade its weapons systems. Similar casualty figures were previously cited by U.K. Defense Intelligence in June.
Kursk Oblast borders Ukraine’s Sumy Oblast. In August 2024, Ukrainian forces launched a cross-border incursion into the region, capturing approximately 1,300 square kilometers of Russian territory in the initial months of the operation. The move was reportedly aimed at diverting Russian forces from eastern Ukraine and disrupting plans for a possible offensive into Sumy Oblast.
Russia later mounted a counteroffensive, reinforced by roughly 12,000 North Korean troops, which pushed Ukrainian forces out of most of the captured territory.
Ukrainian forces are taking advantage of recent blocks on Starlink terminals and Telegram and conducting counterattacks near the Dnipropetrovsk-Zaporizhzhia Oblast administrative border
Geolocated footage published on February 12 shows Russian strikes against static Ukrainian positions east of the Haichur River, including east of and in southern Dobropillya and north of Varvarivka (both northwest of Hulyaipole).[9] This footage indicates that Ukrainian forces likely maintained control of these positions prior to February 12 and are likely using localized counterattacks to reconnect these frontline positions to each other. Russian forces likely bypassed these Ukrainian positions during infiltration missions to exaggerate the extent of Russian gains in the area.
ISW began observing reports of limited and localized Ukrainian counterattacks near the Dnipropetrovsk-Zaporizhzhia Oblast administrative border on February 9. Russian milbloggers initially portrayed these counterattacks as a broader Ukrainian “counteroffensive,” but Ukrainian military sources and some Russian milbloggers have since indicated that the Ukrainian counterattacks are limited in scale and span.[11] Russian milbloggers have continued to claim that Ukrainian forces are conducting counterattacks north and northwest of Hulyaipole, but noted that the situation on the ground is unclear due to degraded Russian communications on the frontline.
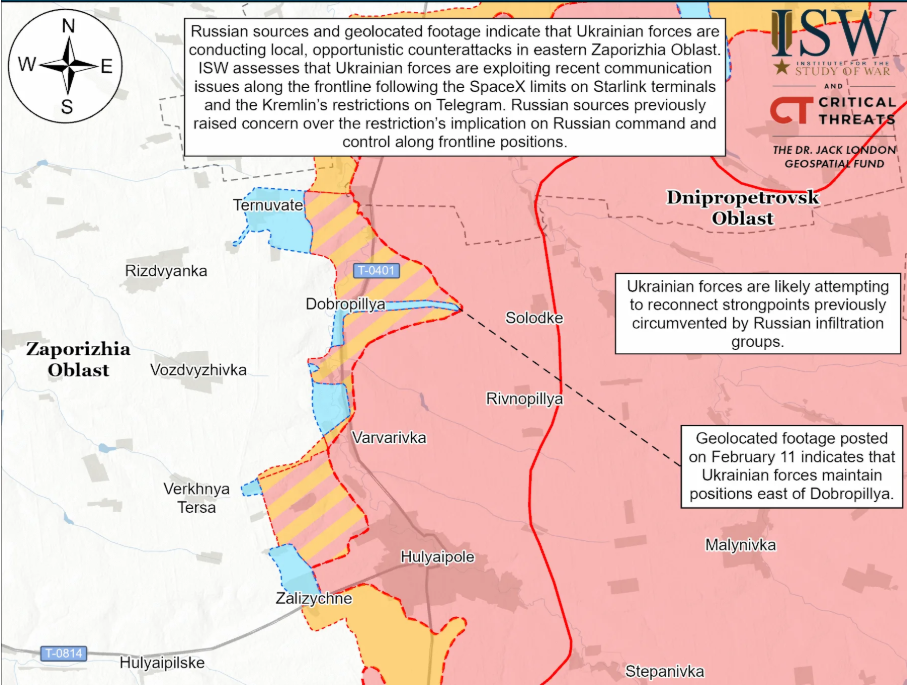
Ukrainian tactical counterattacks in this area are likely an opportunistic response to favorable battlefield conditions. A senior NATO official told the BBC’s Russia service on February 11 that at least some of the Ukrainian battlefield successes in eastern Zaporizhzhia Oblast are due to SpaceX’s efforts to prevent Russian forces from using Starlink terminals in early February 2026. A Kremlin-affiliated Russian milblogger claimed that there are “new complicating factors” to Russian communication issues from restrictions on Russian Starlink access. The milblogger is likely alluding to Russia’s restrictions on the use of Telegram since February 9, which Russian forces on the frontline have also used for communications. Russian milbloggers have been warning that the Kremlin’s decision to block Telegram at the same time as SpaceX’s restrictions on Russian Starlink usage will severely impact Russian communications in the near-term. Ukrainian counterattacks in the Dnipropetrovsk-Zaporizhzhia Oblast border area likely seek to exploit these recent Russian communication and command-and-control (C2) challenges.
Russia attacked Ukraine with 154 drones and Iskander-M missiles overnight
Russian forces launched a large-scale overnight attack on Ukraine on February 12–13, deploying an Iskander-M ballistic missile and 154 loitering munitions, including Shahed, Gerbera, and Italmas drones, Ukraine’s Air Force Command reported. Approximately 100 of the drones were identified as Shahed-type attack UAVs.
By 8:30 a.m., Ukrainian air defence units had shot down or jammed 111 drones of various types. Authorities reported that the Iskander-M missile and 22 loitering munitions struck targets at 18 locations, while debris from intercepted aerial threats fell at two additional sites.
Ukraine’s defence forces used aircraft, surface-to-air missile systems, electronic warfare assets, unmanned systems units and mobile fire groups to repel the assault. The attack was still ongoing in the morning hours, with several Russian drones remaining in Ukrainian airspace.
Russian strike on Kramatorsk killed three brothers and injured two
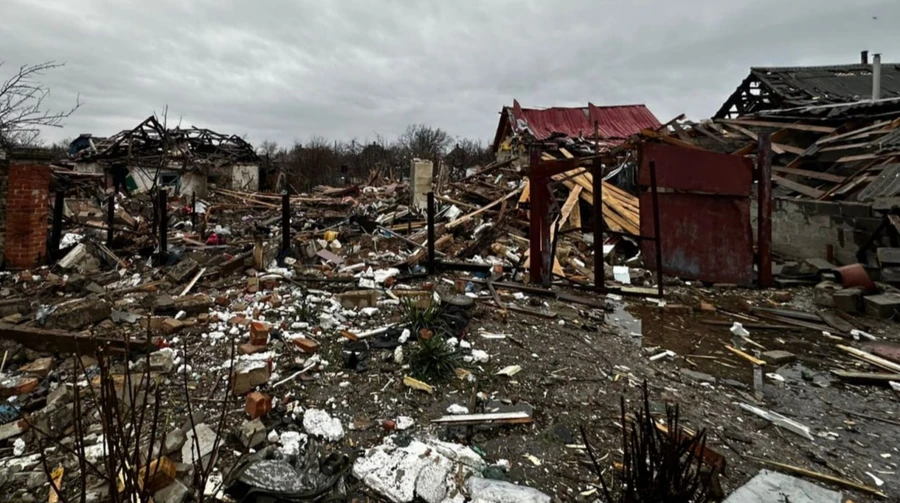

Russian strike on the city of Kramatorsk in Donetsk Oblast on the evening of February 12 resulted in four dead civilians, according to the Donetsk Oblast Prosecutor’s Office. The attack reportedly targeted a residential area at around 9:15 p.m., resulting in a direct hit on a private house.
Initial reports indicated that two 19-year-old brothers and their eight-year-old sibling were killed in the strike. Their 43-year-old mother and 65-year-old grandmother were injured and hospitalized with blast injuries, concussions, and multiple contusions affecting the chest, spine, and arm. Authorities said the women received medical treatment.
In a later update, Kramatorsk City Council confirmed that the death toll had risen to four. Mayor Oleksandr Honcharenko said the victims included a child aged approximately eight or nine, two men aged around 30, and a man aged about 63. Local officials said efforts were ongoing to assess the full extent of the damage and consequences of the attack.
Russia confirmed $12 trillion pitch to Trump tied to Ukraine deal — White House remains silent
On February 13, Russia appeared to confirm the existence of a sweeping U.S.–Russia economic proposal known in Kyiv as the “Dmitriev package,” days after President Volodymyr Zelensky publicly disclosed it. A week ago, Zelensky said that Ukrainian intelligence had briefed him on what he described as a roughly $12 trillion framework for large-scale economic cooperation between Moscow and Washington. He linked the proposal to Kirill Dmitriev, head of Russia’s sovereign wealth fund, who has remained in contact with senior U.S. officials, including Special Envoy Steve Witkoff. The White House declined to confirm the existence of such proposals following Zelensky’s remarks and subsequent reporting by Bloomberg.
February 12 report, Bloomberg cited an internal Russian memo outlining Moscow’s interest in securing broad economic cooperation with the United States as part of a potential arrangement tied to ending the war in Ukraine. According to the report, Russia is seeking relief from financial restrictions that have cut it off from the dollar payment system and views the restoration of dollar-based settlements as part of a possible peace framework. The memo reportedly lists seven areas of cooperation, including long-term contracts for American aircraft to modernize Russia’s commercial fleet, joint ventures in hard-to-extract oil and liquefied natural gas production, expanded nuclear energy cooperation, and mining projects focused on lithium, copper, nickel, and platinum. Moscow is also said to be offering preferential treatment to returning U.S. firms and proposing joint efforts to promote fossil fuels globally.
Today, when Kremlin spokesperson Dmitry Peskov was asked about the package, he did not deny its existence, describing economic cooperation as a natural extension of shared business interests. His comments marked the first public acknowledgment from Moscow that such proposals are under discussion. The reported plan highlights Russia’s interest in restoring dollar transactions despite years of rhetoric from President Vladimir Putin criticizing U.S. currency dominance and promoting stepping away from the US dollar through expanded use of national currencies and mechanisms within the BRICS bloc. Analysts say the proposal suggests Moscow may be linking progress on Ukraine not only to territorial and political demands but also to a broader reset of economic relations with Washington, using the war as leverage in negotiations.

